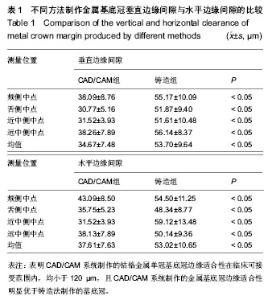
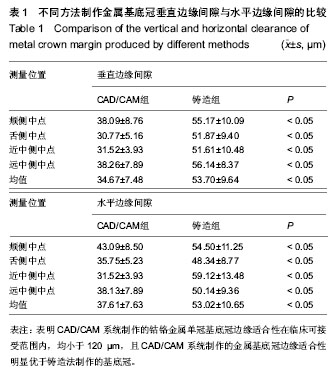
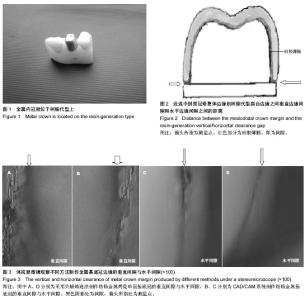
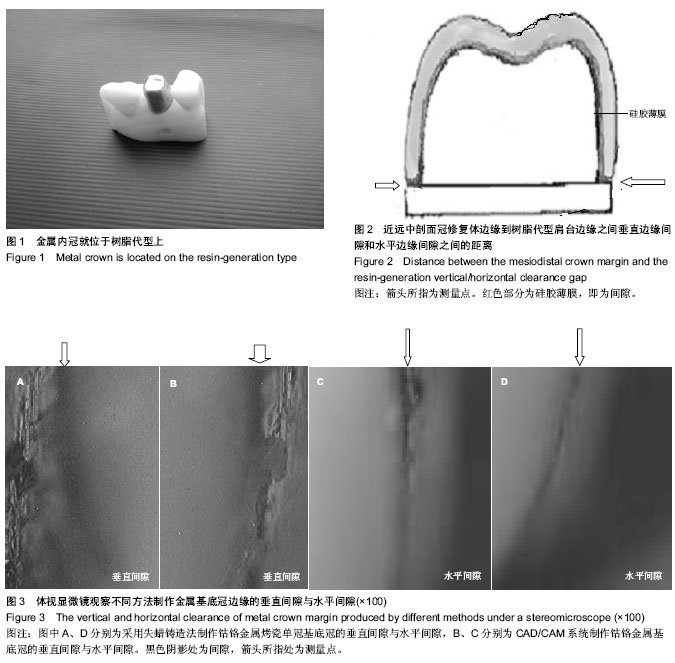
| [1] Sjögren G,Molin M,van Dijken JW.A 10-year prospective evaluation of CAD/CAM-manufactured (Cerec) ceramic inlays cemented with a chemically cured or dual-cured resin composite.Int J Prosthodont.2004;17(2):241-246.
[2] Liu PR.A panorama of dental CAD/CAM restorative systems.Compend Contin Educ Dent. 2005;26(7): 507-508, 510,512 passim; quiz 517, 527.
[3] 陈冶清.口腔材料学[M].3版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2003:169.
[4] Kikuchi M, Okuno O.Machinability evaluation of titanium alloys.Dent Mater J. 2004;23(1):37-45.
[5] 邱宏亮.CAD/CAM二氧化锆全瓷冠修复对牙周健康状况影响的临床研究[J].中国医疗前沿,2009,7(23):69.
[6] Tan PL,Gratton DG,Diaz-Arnold AM,et al.An In Vitro Comparison of Vertical Marginal Gaps of CAD/CAM Titanium and Conventional Cast Restorations.J Prosthodont. 2008; 17(5): 378-383.
[7] Zhang Z,Tamaki Y,Hotta Y,et al.Novel method for titanium crown casting using a combination of wax patterns fabricated by a CAD/CAM system and a non-expanded investment.Dent Mater.2006;22(7):681-687.
[8] Han HS,Yang HS,Lim HP,et al.Marginal accuracy and internal fit of machine-milled and cast titanium crowns.J Prosthet Dent. 2011;106(3):191-197.
[9] Biscaro L,Bonfiglioli R,Soattin M,et al.An in vivo evaluation of fit of zirconium-oxide based ceramic single crowns, generated with two CAD/CAM systems, in comparison to metal ceramic single crowns.J Prosthodont.2013;22(1):36-41.
[10] Bindl A,Mörmann WH.Marginal and internal fit of all-ceramic CAD/CAM crown-copings on chamfer preparations.J Oral Rehabil.2005;32(6):441-447.
[11] Witkowski S,Komine F,Gerds T.Marginal accuracy of titanium copings fabricated by casting and CAD/CAM techniques.J Prosthet Dent.2006;96(1):47-52.
[12] 徐君伍.口腔修复学[M].4版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2000:48.
[13] 长谷川二郎,齿科技工别册,昭和55年7月.
[14] Syrek A,Reich G,Ranftl D,et al.Clinical evaluation of all-ceramic crowns fabricated from intraoral digital impressions based on the principle of active wavefront sampling.J Dent.2010;38(7):553-559.
[15] Holmes JR,Bayne SC,Holland GA,et al.Considerations in measurement of marginal fit.J Prosthet Dent. 1989;62(4): 405-408.
[16] Hunter AJ,Hunter AR.Gingival margins for crowns: a review and discussion. Part II: Discrepancies and configurations.J Prosthet Dent.1990;64(6):636-642.
[17] Yan M,Takahashi H.Titanium casting using commercial phosphate-bonded investments with quick heating method. Dent Mater J.2006;25(2):391-398.
[18] 白石柱,马秦,雷德林,等.CAD/CAM 技术在游离腓骨瓣移植重建下颌骨中的应用[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2010,26(4):486-490.
[19] Chen Y, Miao X Thermal and chemical stability of fluorohydroxyapatite ceramics with different fluorine contents.Biomaterials.2005;26(11):1205-1210.
[20] 陈熙,程辉,马守治,等.不同冠边缘形式的非贵金属金瓷冠边缘适合性的研究[J].口腔颌面修复学杂志,2007,8(2):111-114.
[21] 吴伟利,张修银.全瓷冠边缘适合性研究进展[J].口腔材料器械杂志,2007,16(4):200-204.
[22] 杨军成,郑光勇.应用反求与快速成型技术整复下颌骨缺损[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2009,26(2):441-442.
[23] May KB ,Russell MM,Razzoog ME,et al.Precision of fit : The procera all ceram crown. J Prosthet Dent. 1998;80(4): 394-404.
[24] Boening KW,Wolf BH,Schmidt AE,et al.Clinical fit of Procera All Ceram crowns.J Prosthet Dent. 2000;84(4): 419-424.
[25] Beuer F,Edelhoff D,Gernet W,et al.Effect of preparation angles on the precision of zirconia crown copings fabricated by CAD/CAM system.Dent Mater J. 2008;27(6):814-820.
[26] Baig MR,Tan KB,Nicholls JI.Evaluation of the marginal fit of a zirconia ceramic computer-aided machined (CAM) crown system.J Prosthet Dent.2010;104(4):216-227.
[27] Akbar JH,Petrie CS,Walker MP,et al.Marginal adaptation of Cerec 3 CAD/CAM composite crowns using two different finish line preparation designs.J Prosthodont. 2006;15(3): 155-163.
[28] Christensen GJ. Marginal fit of gold inlay castings. J Prosthet Dent.1966;16(2):297-305;
[29] Schaefer O,Watts DC,Sigusch BW,et al.Marginal and internal fit of pressed lithium disilicate partial crowns in vitro: a three-dimensional analysis of accuracy and reproducibility. Dent Mater.2012;28(3):320-326.
[30] Lofstrom LH,Barakat MM.Scanning electron microscopic evaluation of clinically cemented cast gold restorations.J Prosthet Dent.1989;61(6):664-669.
[31] 湛渝,马丁,李涛.668颗后牙镍铬合金PFM边缘适合性的临床观察[J].口腔颌面修复学杂志,2007,8(3):169-170.
[32] Kurtzman GM,Dompkowski DE.Using digital impressions and CAD/CAM in implant dentistry.Dent Today. 2014;33(3):114, 116-117.
[33] Parpaiola A,Norton MR,Cecchinato D,et al.Virtual abutment design: a concept for delivery of CAD/CAM customized abutments--report of a retrospective cohort.Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent.2013;33(1):51-58.
[34] Tripodakis AP,Gousias HC,Andritsakis PD,et al.Evaluation of alternative approaches in designing CAD/CAM frameworks for fixed partial dentures.Eur J Esthet Dent. 2013;8(4): 546-556.
[35] Schultheis S,Strub JR,Gerds TA,et al.Monolithic and bi-layer CAD/CAM lithium-disilicate versus metal-ceramic fixed dental prostheses: comparison of fracture loads and failure modes after fatigue.Clin Oral Investig. 2013;17(5):1407-1413.
[36] Karl M,Graef F,Wichmann M,et al.Microfractures in metal-ceramic and all-ceramic implant-supported fixed dental prostheses caused by superstructure fixation.Dent Mater J. 2012;31(3):338-345.
[37] Marghalani TY,Hamed MT,Awad MA,et al.Three-dimensional finite element analysis of custom-made ceramic dowel made using CAD/CAM technology.J Prosthodont. 2012;21(6): 440-450.
[38] Vigolo P,Mutinelli S.Evaluation of zirconium-oxide-based ceramic single-unit posterior fixed dental prostheses (FDPs) generated with two CAD/CAM systems compared to porcelain-fused-to-metal single-unit posterior FDPs: a 5-year clinical prospective study.J Prosthodont.2012;21(4):265-269.
[39] Maló P,de Araújo Nobre M,Borges J,et al.Retrievable metal ceramic implant-supported fixed prostheses with milled titanium frameworks and all-ceramic crowns: retrospective clinical study with up to 10 years of follow-up.J Prosthodont. 2012;21(4):256-264.
[40] Miyazaki T, Hotta Y.CAD/CAM systems available for the fabrication of crown and bridge restorations.Aust Dent J. 2011;56 Suppl 1:97-106.
[41] Baig MR,Rajan G,Rajan M.Edentulous arch treatment with a CAD/CAM screw-retained framework and cemented crowns: a clinical case report.J Oral Implantol. 2009;35(6):295-299.
[42] Tao J,Han D.The effect of finish line curvature on marginal fit of all-ceramic CAD/CAM crowns and metal-ceramic crowns. Quintessence Int.2009;40(9):745-752.
[43] Kim S,Kim HI,Brewer JD,et al.Comparison of fracture resistance of pressable metal ceramic custom implant abutments with CAD/CAM commercially fabricated zirconia implant abutments.J Prosthet Dent.2009;101(4):226-230.
[44] Vigolo P,Fonzi F.An in vitro evaluation of fit of zirconium-oxide-based ceramic four-unit fixed partial dentures, generated with three different CAD/CAM systems, before and after porcelain firing cycles and after glaze cycles.J Prosthodont. 2008;17(8):621-26. |